Difference between revisions of "Watchdog"
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:4.0.0-watchdog.png|thumb|Watchdog diagram]] |
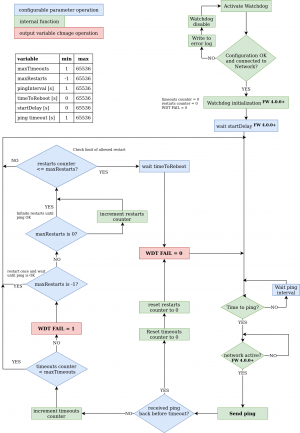
| − | Watchdog is a | + | Watchdog is a function periodically pinging to one defined IP address or URL. It's periodically checking reply from defined IP device by ping (ICMP). You can monitor physical presence of the IP device or Internet connectivity. You can use several WatchDog functions in parallel. |
| − | + | Based on each Watchdog state one or several RULEs can be executed. Each [https://wiki.netio-products.com/index.php?title=Rules '''Rule'''] can perform several actions (Set Output, Short Off (restart) output, Toggle output or send Alarm state to the NETIO Cloud service. Based on this Alarm state can NETIO Cloud send email to defined recipient. All Watchdogs are listed in the JSON protocol wit their current states. It can be used by 3rd party software. | |
| + | |||
| + | Each Watchdog function state is the <code>FAIL</code> variable. | ||
| + | * Watchdog '''Fail = FALSE''' = ping answer is '''OK''' | ||
| + | * Watchdog '''Fail = TRUE''' = ping answer '''not received''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <sup><code>FW 4.0.0+</code></sup>Once network connection is not active the watchdog is not in operation. To detect these stater use Connectivity events in RULES. | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 35: | Line 41: | ||
| maxRestarts | | maxRestarts | ||
| int | | int | ||
| − | | Maximum number of restarts when an error condition is declared. After this limit is reached, the | + | | Maximum number of restarts when an error condition is declared. After this limit is reached, the WatchDog remains in an <code>FAIL=TRUE</code> state until the next successful ping. |
| − | If set to 0, the | + | If set to 0, WatchDog will restart output (trigger rule) after each FAIL=TRUE is declared and not only if FAIL status is changed (This can cause indefinite restarts when the ping remains unsuccessful). |
| + | |||
| + | If set to -1, WatchDog will restart output (trigger rule) only once and then remains in FAIL=TRUE state until next successful ping. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | startDelay | ||
| + | | int | ||
| + | | Starting delay in seconds at watchdog startup.(Enable or device power up)<sup><code>FW 4.0.0+</code></sup> | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Example:</b> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "target": "192.168.101.130", | ||
| + | "pingInterval": 5, | ||
| + | "timeout": 1, | ||
| + | "maxTimeouts": 2, | ||
| + | "timeToReboot": 10, | ||
| + | "maxRestarts": -1, | ||
| + | "startDelay": 0 | ||
| + | } | ||
Latest revision as of 20:01, 19 June 2023
Watchdog is a function periodically pinging to one defined IP address or URL. It's periodically checking reply from defined IP device by ping (ICMP). You can monitor physical presence of the IP device or Internet connectivity. You can use several WatchDog functions in parallel.
Based on each Watchdog state one or several RULEs can be executed. Each Rule can perform several actions (Set Output, Short Off (restart) output, Toggle output or send Alarm state to the NETIO Cloud service. Based on this Alarm state can NETIO Cloud send email to defined recipient. All Watchdogs are listed in the JSON protocol wit their current states. It can be used by 3rd party software.
Each Watchdog function state is the FAIL variable.
- Watchdog Fail = FALSE = ping answer is OK
- Watchdog Fail = TRUE = ping answer not received
FW 4.0.0+Once network connection is not active the watchdog is not in operation. To detect these stater use Connectivity events in RULES.
Structure
| Variable | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| target | IP / URL | Monitored address |
| pingInterval | int | [s] Time interval between pings |
| timeout | int | [s] Time waiting for answer |
| maxTimeouts | int | Number of failed pings required to evaluate to FAIL=TRUE
|
| timeToReboot | int | [s] Time the Watchdog waits after announcing an error condition before starting a new cycle |
| maxRestarts | int | Maximum number of restarts when an error condition is declared. After this limit is reached, the WatchDog remains in an FAIL=TRUE state until the next successful ping.
If set to 0, WatchDog will restart output (trigger rule) after each FAIL=TRUE is declared and not only if FAIL status is changed (This can cause indefinite restarts when the ping remains unsuccessful). If set to -1, WatchDog will restart output (trigger rule) only once and then remains in FAIL=TRUE state until next successful ping. |
| startDelay | int | Starting delay in seconds at watchdog startup.(Enable or device power up)FW 4.0.0+
|
Example:
{
"target": "192.168.101.130",
"pingInterval": 5,
"timeout": 1,
"maxTimeouts": 2,
"timeToReboot": 10,
"maxRestarts": -1,
"startDelay": 0
}